Light bulbs have been lighting up our world for over a hundred years, but do we really understand how they work? When you go to the store to buy a replacement bulb, the box labels are filled with numbers and industry terms that can leave you wondering how to know which bulb you actually need.
Fortunately, understanding the difference between lumens and watts is fairly straightforward. Take a quick minute to read this quick summary, and you’ll be ready to hit the stores to find exactly what you need.

Lumens
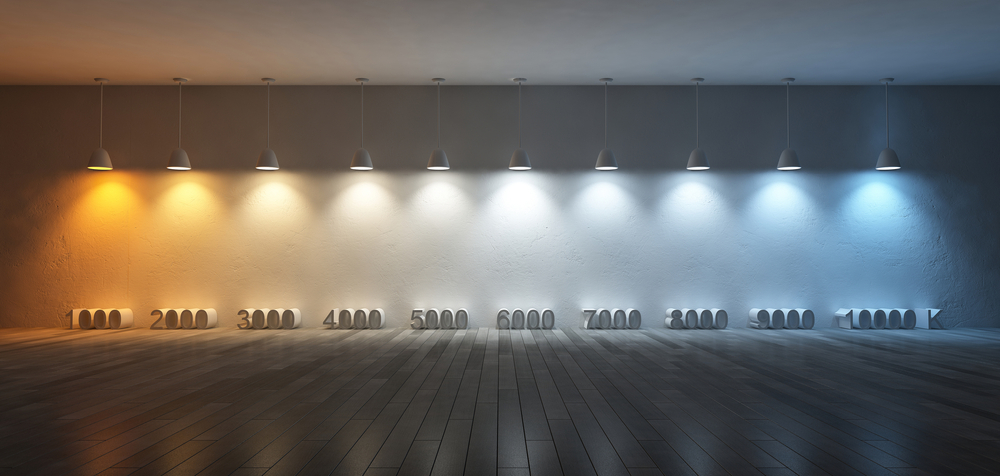
Lumens measure the amount of light a bulb emits. The technical definition is “the unit of luminous flux, equal to the luminous flux emitted in a unit solid angle by a point source of one candle intensity.” In less scientific terms, the higher the lumen rating, the brighter the bulb. Most mainstream bulb labels use the full term, but if you can’t find the word “lumens” on the label look for its abbreviation, lm.
How many lumens do I need?
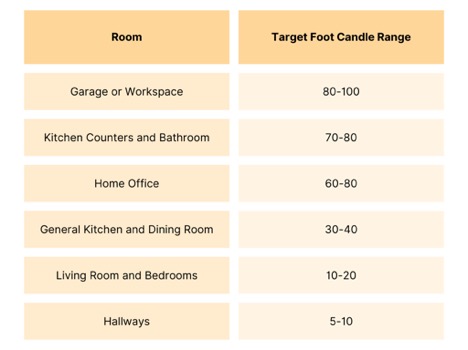
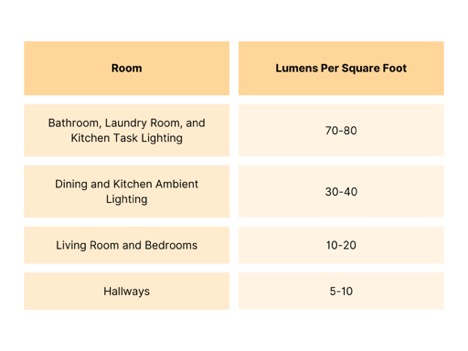
Contrary to popular belief, you shouldn’t put the brightest bulbs you can find in every area of your home. The rooms in your home will all need different levels of light, depending on how you use them. Use bulbs with a high lumen count in areas where you need a much brighter light, like above your kitchen counters. You need much less light in your bedroom, so consider going with lower lumen count bulbs in warmer colors to keep it a relaxing space where you can get some sleep.
While there are complicated equations out there that you can use to calculate your “exact” lumen requirements, the trouble is that every person and every space is different. You may find that you prefer brighter lights than what’s “necessary” in one place and dimmer lights in another. Your best bet is to try a few different bulbs, or better yet – get a dimmer switch so that you can customize your light levels depending on your needs for the day.
Pro Tip: Lumens can be added across several light sources in a space. It’s not an exact science because it doesn’t take into account distance from the source and the angles of the light, but if you have three 800lm bulbs in a room, it will be lit with roughly 1800lm.

Watts
Watts measure the amount of power consumed by the bulb. One watt isn’t much, it’s equal to 1/746 horsepower. It’s named after James Watt, a Scottish inventor credited for creating a steam engine during the Industrial Revolution. The symbol for watts is “W”.
Most electrical devices are rated in watts, although large appliances that use more power are often measured in kilowatts, which is equal to one thousand watts. (1W = 1000kW)
The wattage of a bulb will tell you only how much power it consumes, not how bright it is. The lower the watt rating on the bulb, the cheaper it will be on your energy bill to light your house.
Before you buy, always check your light fixture for its watt rating. Never put a bulb with a higher watt rating than the fixture can handle. If the bulb tries to pull more power than the fixture can handle, it could start a fire.
Energy-Efficient Bulbs
Before the days of LED bulbs, it was pretty easy to get a good idea of how bright a bulb was by simply looking at the wattage. The higher the watts, the brighter the bulb. LED lightbulbs can give off the same amount of light as a traditional bulb using far fewer watts. This is what the labels mean when they say the bulbs are “energy efficient” – they need less power to provide equivalent light.

TL;DR Lumens and Watts
Lumens and Watts both describe how a lightbulb works. Lumens measure the amount of light a bulb emits – the higher the lumens the brighter the bulb. Watts measure the amount of power a light bulb uses. Newer light bulbs like LEDs can produce a lot of light (lumens) using very little power (watts), making them more energy-efficient.
——–
Need help finding the right light bulb? Give the experts at Western Chandelier a call!



















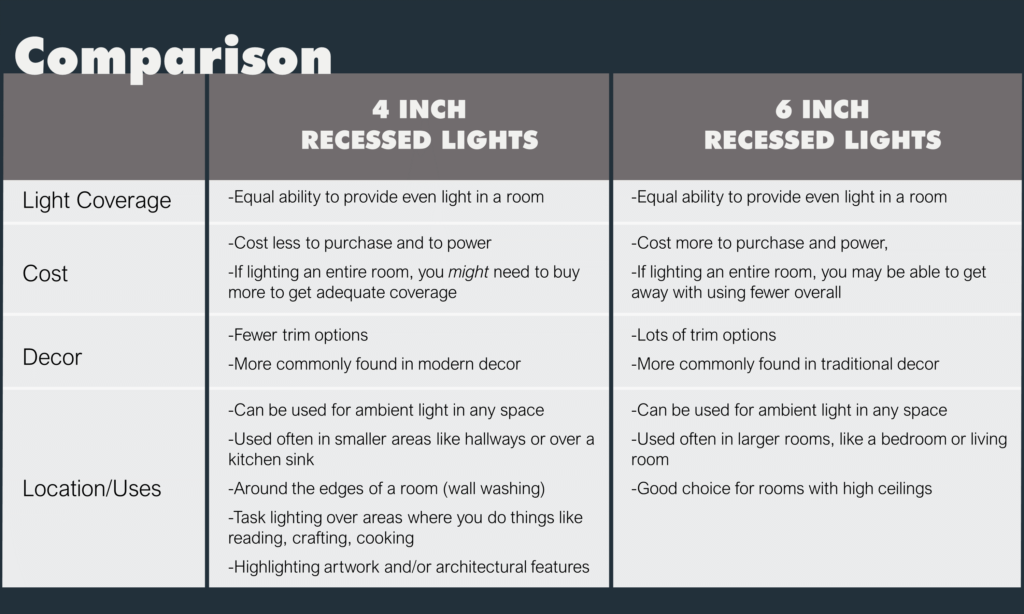







 Diffused light is a natural companion to warm light. This term refers to light that is scattered and doesn’t cast a hard shadow. You can create this effect through reflected or covered lighting. We’ll focus on the latter here and touch more on reflected light in the next section.
Diffused light is a natural companion to warm light. This term refers to light that is scattered and doesn’t cast a hard shadow. You can create this effect through reflected or covered lighting. We’ll focus on the latter here and touch more on reflected light in the next section.












